Elbow Joint Pain: Causes and Management
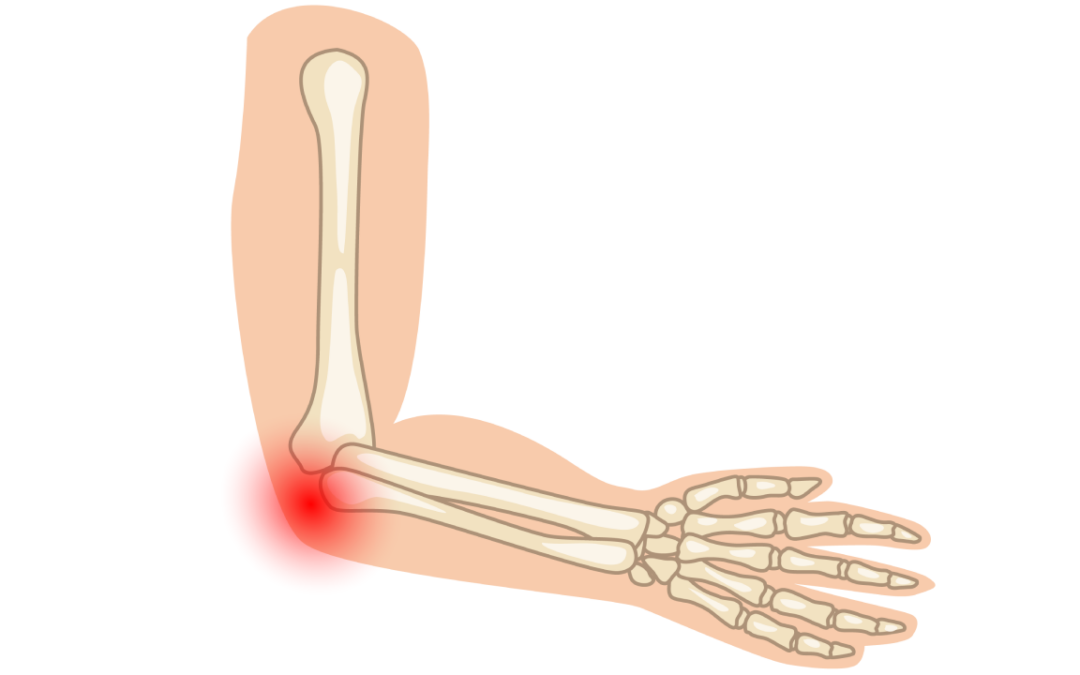
The elbow joint is the point where three long bones of the arm meet, located at the middle portion of the arm. The humerus, the bone of the upper arm, meets the radius and ulna, the two bones of the lower arm. The elbow joint is a hinge joint, meaning its range of motion is limited to forward and backward movement, similar to a door.
The bones are connected to their respective muscles, enabling movement. The structures involved in the elbow joint include:
– Humerus: bone of the upper arm
– Radius: outer bone of the forearm
– Ulna: inner bone of the forearm
– Cartilage: soft portions of the ends of bones that help form joints
– Biceps: muscle that flexes the elbow hinge
– Triceps: muscle that extends the elbow hinge
– Lateral epicondyle: outer bone of the elbow and part of the humerus bone
– Medial epicondyle: inner bone of the elbow and part of the humerus bone
– Tendons: connective tissues that attach muscles to bones
– Ligaments: connective tissues that help attach bones to bones to form joints
– Bursa: fluid-filled sac at the tip of the elbow
Elbow joint pain can result from injury or inflammation to any of these bones, muscles, tendons, or bursa.
Common Causes of Elbow Joint Pain
1. Tennis Elbow: Inflammation of the tendons attaching muscles to the lateral epicondyle, often caused by repetitive forearm motions.
2. Golfer’s Elbow: Inflammation of the tendons attaching muscles to the medial epicondyle, often caused by movements like golf swings.
3. Olecranon Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa at the tip of the elbow, often caused by injury or minor trauma.
4. Fractures: Breaks in the bones associated with the elbow joint, often requiring casts, immobilization, or surgical treatment.
5. Sprains: Tears or stretches of ligaments, often caused by overextension or collision.
6. Arthritis of the Elbow: Inflammation of the elbow joint, often caused by various types of arthritis, such as gouty arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or osteoarthritis.
7. Cellulitis: Infection and inflammation of the skin, often caused by bacteria entering through open wounds.
8. Disease of Cartilage: Flaking away of the soft ends of bones, often causing immobility, pain, and loss of range of motion.
9. Entrapment of the Ulnar Nerve: Compression of the ulnar nerve, often causing numbness, tingling, and pain in the forearm and hand.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for elbow joint pain depends on the underlying cause. Common management strategies include:
– Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications
– Physical therapy and exercises
– Immobilization and casting
– Surgical treatment
– Antibiotics for infections
It’s essential to consult a doctor if you experience elbow joint pain to receive proper diagnosis and treatment.
References
https://www.medicinenet.com/elbow_pain/article.htm
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/guide/elbow-pain#1
https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/elbow-pain/basics/causes/sym-20050874
https://www.versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/conditions/elbow-pain/
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003172.htm