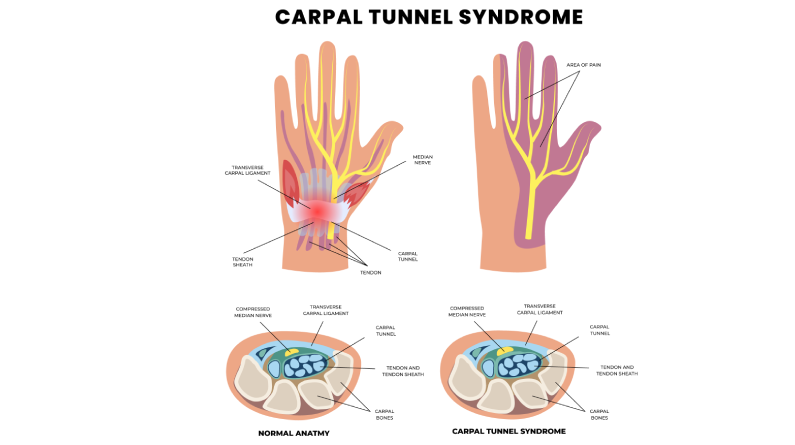
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, is compressed or squeezed. This compression can cause a range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and wrist.
Anatomy of the Wrist
The wrist joint is made up of several components, including:
– Carpal bones (8 small bones in the wrist)
– Radius bone (long bone of the forearm)
– Metacarpal bones (long bones in the palm)
– Articular cartilage (cartilage between the joints)
– Ligaments (soft tissues that connect bones to bones)
– Tendons (connect muscles to bones)
– Synovial fluid (lubricating fluid in the joint capsule)
– Nerves (radial, median, and ulnar nerves)
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The median nerve controls sensation and movement in the hand and wrist. Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome may include:
– Burning, tingling, numbness, or itching in the palm, thumb, index, and middle fingers
– Weakness in the affected hand
– Sudden shock-like sensations in the fingers and thumb
– Dropping things due to weakness or numbness
– Trouble holding or grasping objects
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is often caused by a combination of factors, including:
– Heredity (smaller carpal tunnel)
– Repetitive hand and wrist movements
– Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause
– Certain health conditions (diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid problems)
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
To diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome, a doctor may:
– Perform a physical examination and medical history
– Order X-rays of the wrist
– Conduct electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies
– Perform a flexion test (bending the wrist)
– Check for Tinel’s sign (tingling sensation in fingers when the median nerve is tapped)
Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome may include:
– Supportive treatments:
– Wearing a wrist splint at night
– Pain-killers
– Cortisone injection
– Heat treatments
– Work-place changes:
– Raising or lowering the office chair
– Changing the position of the computer keyboard
– Exercises:
– Flexion and extension exercises
– Physiotherapy using machines
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be recommended if:
– Symptoms are severe and persistent
– Nerve damage is detected
– Conservative treatments are ineffective
The goal of surgery is to relieve pressure on the median nerve by:
– Cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel
– Enlarging the tunnel to accommodate the nerve
Prevention
To prevent carpal tunnel syndrome:
– Take regular breaks to stretch and move around
– Maintain good posture and wrist alignment
– Avoid bending or twisting the wrist
– Use ergonomic equipment and tools
– Stay physically active and healthy
Conclusion
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and disability. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals take steps to prevent and manage the condition. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.