Understanding Sciatica: Causes, Symptoms, and Pain Relief
Sciatica is a common condition characterized by pain, numbness, and tingling in the lower back and legs. It occurs when the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the human body, is irritated or compressed.
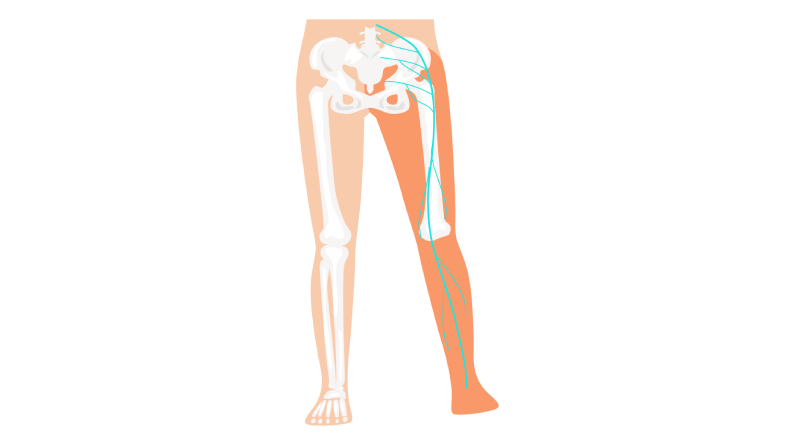
What is the Sciatic Nerve?
The sciatic nerve begins in the lower portion of the spinal cord, travels through the pelvis, and extends down to the lower limb. It plays a crucial role in controlling muscle movement and sensation in the legs.
Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Narrowing of the Spinal Canal: Also known as spinal stenosis, this condition can put pressure on the sciatic nerve.
2. Degenerative Disc Disease: Wear and tear on the spinal discs can cause them to bulge or rupture, compressing the sciatic nerve.
3. Spondylolisthesis: This condition occurs when a vertebra slips forward over another one, putting pressure on the sciatic nerve.
4. Muscle Spasm: Muscle spasms in the buttock area can compress the sciatic nerve.
Symptoms of Sciatica
The symptoms of sciatica can vary, but common signs include:
1. Lower Back Pain: Pain that radiates from the lower back down to the legs.
2. Pain on One Side: Pain that occurs on one side of the body, from the lower back down to the leg.
3. Tingling or Burning Sensation: A tingling or burning sensation that runs down the leg.
4. Weakness or Numbness: Weakness or numbness in the leg or foot.
5. Hip Pain: Pain in the hip or buttock area.
Diagnosing Sciatica
Sciatica is typically diagnosed using a combination of:
1. Medical History: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history.
2. Physical Examination: A physical examination to assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation.
3. Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the spine and surrounding tissues.
4. Electromyogram: A test to measure the electrical activity of muscles.
Pain Relief Options
Treatment for sciatica typically involves a combination of:
1. Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and prescription medications.
2. Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches to relieve pain and improve mobility.
3. Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area.
4. Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve compression on the sciatic nerve.
Managing Sciatica
While there is no permanent cure for sciatica, there are several lifestyle changes and techniques that can help manage the condition:
1. Maintaining Good Posture: Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition.
2. Stretching and Exercise: Engaging in regular exercise and stretching to relieve pain and improve mobility.
3. Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to reduce stress and anxiety.
4. Healthy Eating: Maintaining a healthy diet to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
References
https://www.webmd.com/back-pain/treatment-for-sciatica
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12792-sciatica