Understanding Stroke: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
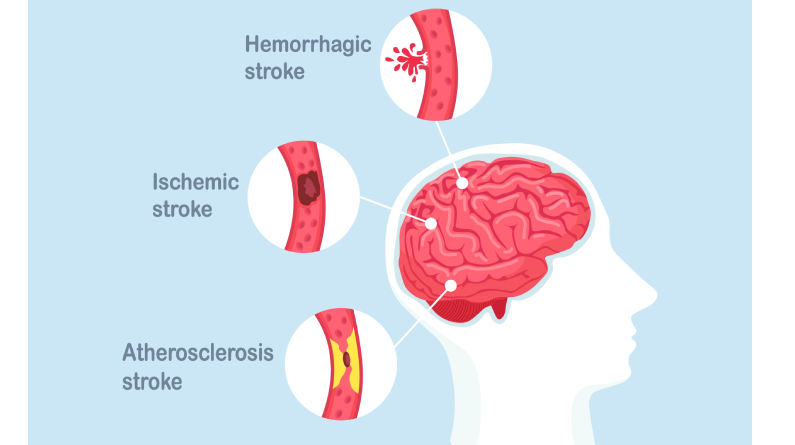
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die within minutes. This can lead to temporary or permanent damage to the parts of the body controlled by the affected area of the brain. There are three main types of strokes:
1. Ischemic Stroke: The most common type, caused by a blockage in the artery supplying blood to the brain.
2. Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Caused by the sudden bursting of an artery within the brain, leading to bleeding and compression of brain structures.
3. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Caused by the sudden bursting of an artery just below the brain’s surface, leading to bleeding into the space surrounding the brain.
Symptoms of Stroke
Symptoms of a stroke appear suddenly and require immediate medical attention to prevent permanent damage. Some people may experience:
– Slurred speech or difficulty speaking
– Difficulty understanding others
– Sudden numbness or paralysis of the face, arm, or leg
– Vision problems, including blurred vision, double vision, or loss of vision
– Severe headache, vomiting, dizziness, or confusion
– Difficulty walking, loss of balance, or coordination
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
A TIA, also known as a mini-stroke, is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. Symptoms are similar to those of a stroke but last only for a short period.
Diagnosis of Stroke
If you suspect someone is having a stroke, call emergency services immediately. Diagnosis involves:
– Physical examination
– Blood tests
– Imaging tests, such as CT scans, MRI scans, and cerebral angiograms
– Echocardiogram to check for blood clots in the heart
Treatment of Stroke
Treatment depends on the type of stroke:
– Ischemic Stroke: Emergency medication to dissolve the blood clot, surgery to remove the clot, or angioplasty and stenting to open blocked arteries.
– Hemorrhagic Stroke: Surgery to repair or remove the damaged blood vessel.
– Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other treatments to help regain lost functions.
Prompt medical attention is crucial in treating stroke and minimizing damage. Remember the acronym “FAST” to recognize the signs of a stroke:
F – Face: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of their face droop?
A – Arm: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S – Speech: Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Is their speech slurred or difficult to understand?
T – Time: Time is of the essence. Call emergency services immediately if you observe any of these symptoms.
Rehabilitation After Stroke
Rehabilitation is a crucial part of the recovery process after a stroke. The goal of rehabilitation is to help the patient regain lost functions and adapt to any permanent changes. Rehabilitation may include:
– Physiotherapy to improve mobility and balance
– Occupational therapy to improve daily functioning
– Speech therapy to improve communication
– Dietary counseling to improve nutrition
– Psychological counseling to cope with emotional changes
Preventing Stroke
While some risk factors for stroke cannot be changed, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
– Manage high blood pressure
– Control diabetes
– Maintain a healthy weight
– Exercise regularly
– Eat a balanced diet
– Quit smoking
– Limit alcohol consumption
Conclusion
Stroke is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of stroke can help you take action to reduce your risk and respond quickly if someone around you is experiencing a stroke.
References:
https://www.medicinenet.com/stroke_symptoms_and_treatment/article.htm
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113
http://www.strokecenter.org/patients/about-stroke/what-is-a-stroke/
https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/types_of_stroke.htm
https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/stroke